10 Essential Cybersecurity Best Practices Every Business Should Implement Today

In today’s digital landscape, protecting sensitive information is more crucial than ever. Cybersecurity best practices are essential for every business to safeguard its data, reputation, and finances. With increasing cyber threats, implementing effective cybersecurity measures can make the difference between a secure operation and a devastating breach. In this article, we will outline 10 essential cybersecurity best practices that every business should implement today.

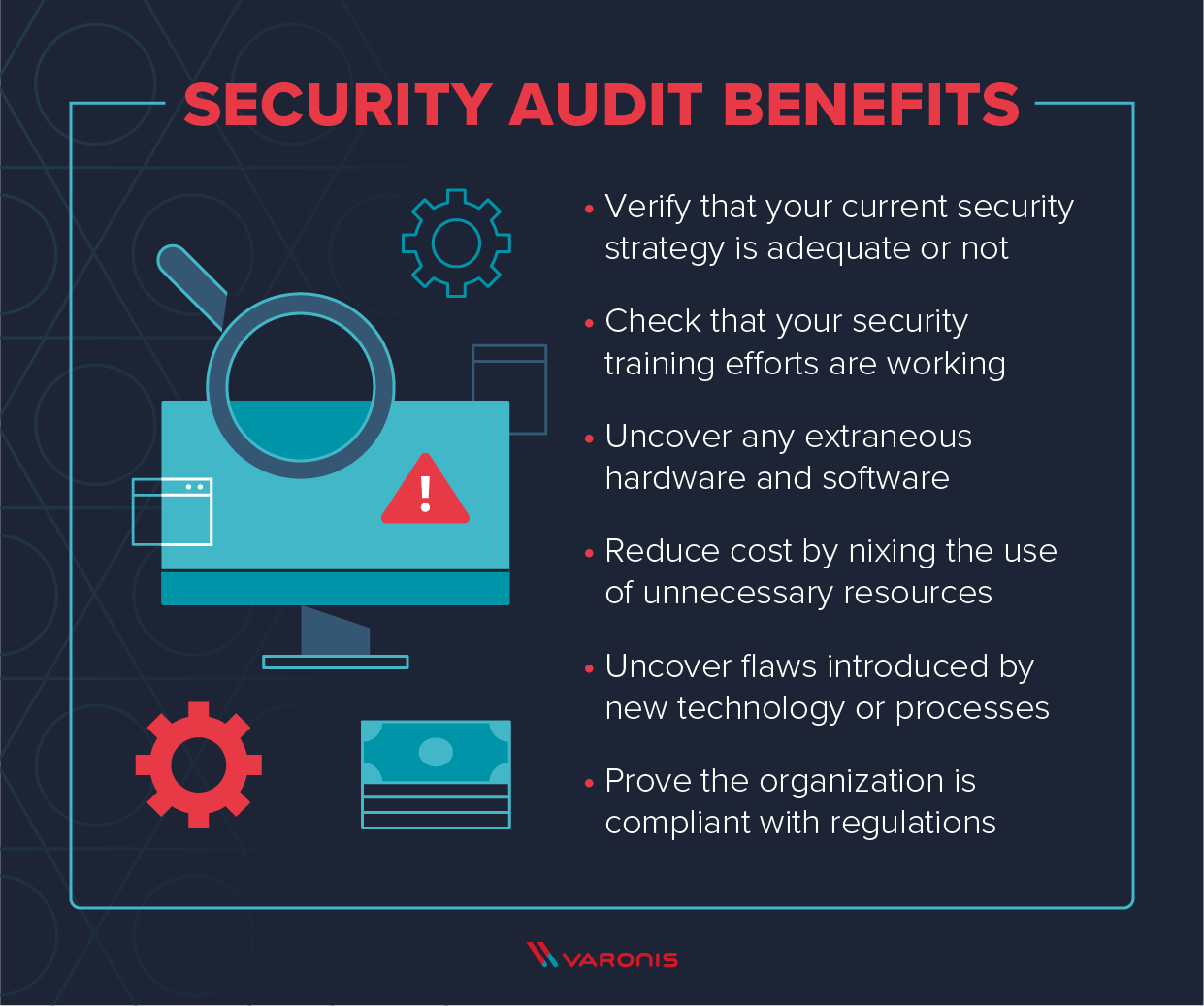
1. Conduct Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits help identify vulnerabilities within your systems. By assessing your current security measures, you can pinpoint areas needing improvement and ensure compliance with industry standards. Audits should include checks for outdated software, weak passwords, and unpatched systems.
2. Use Strong Password Policies
Implementing a strong password policy is one of the simplest yet most effective cybersecurity best practices. Encourage employees to use complex passwords that combine letters, numbers, and symbols. Additionally, require password changes every three to six months and promote the use of password managers.
Using unique passwords for different accounts further enhances security. Consider providing guidelines or resources on creating strong passwords, as many people still opt for easy-to-remember options that are easily cracked.

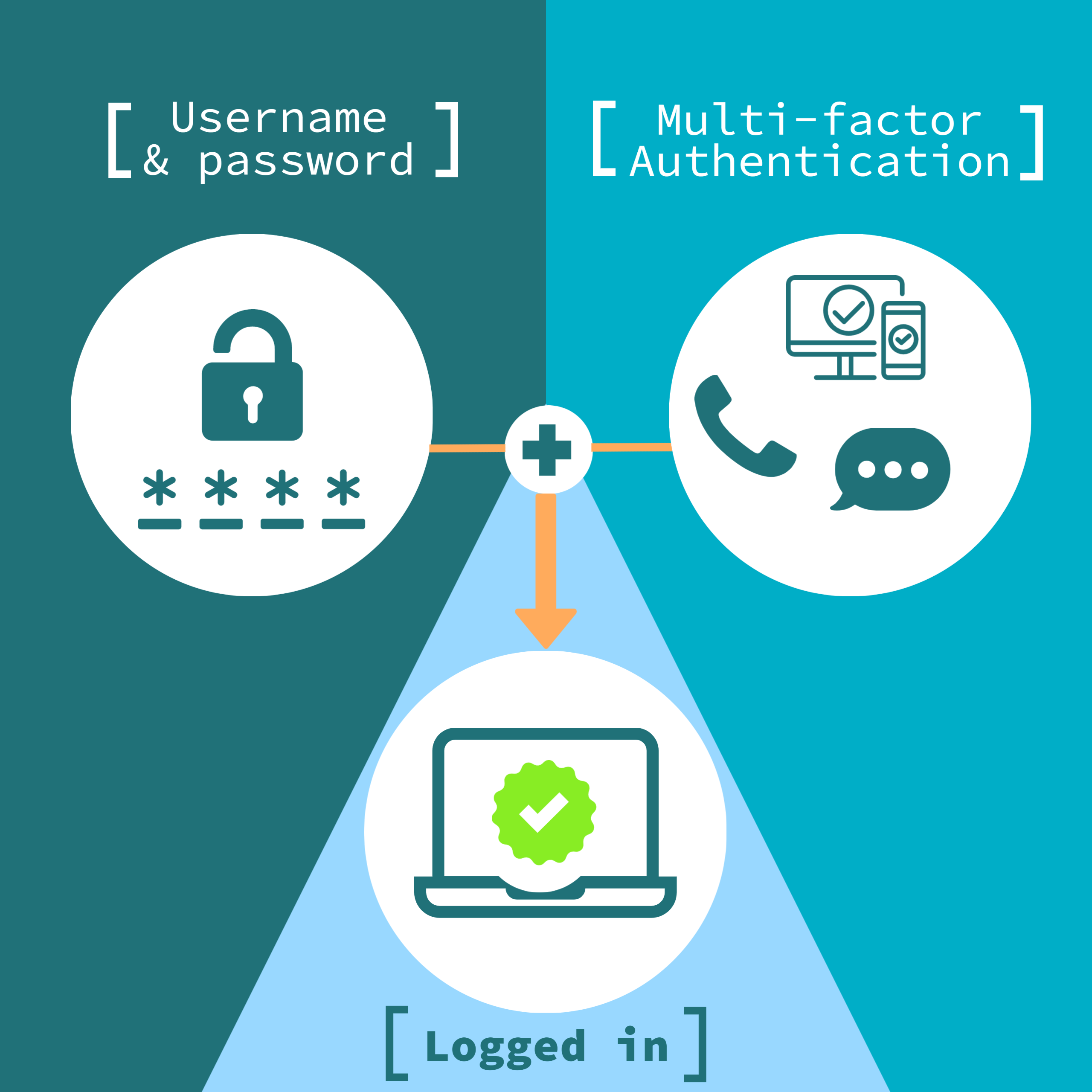
3. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-Factor Authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple means. This could include a password, a text message confirmation, or biometric verification. Implementing MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Businesses should ensure that MFA is enforced not just for sensitive areas but across all company applications. This practice is vital for mitigating the risk of credential theft.
4. Educate Employees on Cybersecurity
Human error is a leading cause of security breaches. Regular training sessions on cybersecurity best practices can help employees recognize phishing attempts, social engineering tactics, and other cyber threats. Ensure that training is ongoing and includes updated information about the latest threats.
Consider conducting simulations to provide hands-on experience in recognizing and responding to phishing attempts. This can help create a culture of vigilance and responsibility regarding cybersecurity.

5. Keep Software and Systems Updated
Outdated software can be a major vulnerability. Regularly update all software, applications, and operating systems to ensure that the latest security patches are applied. Automated updates can be beneficial for maintaining security without manual intervention.
Establish a routine for checking for updates, especially for critical applications. Additionally, educate your team about the importance of updates and how they contribute to overall security.

6. Backup Data Regularly
Regular data backups are crucial in case of a cyberattack or data loss. Implement a backup schedule that includes both local and cloud backups. Test your backup processes regularly to ensure data can be restored quickly and efficiently.
Consider using the 3-2-1 backup strategy: keep three copies of your data, store two backup copies on different storage media, and keep one copy offsite. This approach enhances your data recovery options in the event of a disaster.

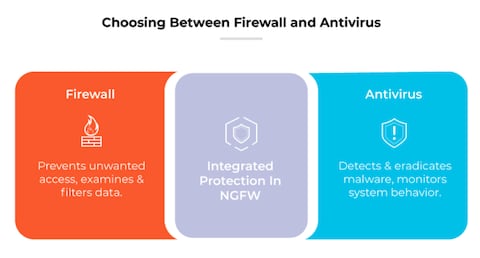
7. Use Firewalls and Antivirus Software
Employing robust firewalls and antivirus software is essential in protecting your network from external threats. Firewalls act as barriers between your internal network and external sources, while antivirus software scans for malicious software and removes potential threats.
Ensure that your firewall settings are properly configured, and regularly update your antivirus software to recognize the latest threats. This combination is a foundational layer of protection against cyberattacks.
8. Limit Access to Sensitive Data
Not all employees need access to all data. Implement role-based access control to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information. Regularly review access permissions and revoke access for employees who no longer require it.
This practice minimizes the risk of insider threats and accidental data exposure. Establish clear policies regarding who can access what information and enforce these policies strictly.
9. Develop an Incident Response Plan
Having an incident response plan in place is vital for quickly addressing any cybersecurity incidents. Your plan should outline the steps to take in the event of a breach, including how to contain the breach, communicate with stakeholders, and restore systems.
Regularly test and update your incident response plan to ensure its effectiveness. Conduct tabletop exercises with your team to practice responding to simulated incidents, which can enhance your organization’s readiness.

10. Monitor Your Systems
Continuous monitoring of your systems helps detect anomalies and potential threats in real-time. Utilize security information and event management (SIEM) tools to gather and analyze security data. Prompt detection and response can mitigate the impact of a cyberattack.
Consider employing threat intelligence solutions to stay updated on emerging threats relevant to your business. Proactive monitoring can help you identify vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Conclusion
Implementing these cybersecurity best practices is essential for safeguarding your business in today’s threat landscape. From conducting regular audits to educating employees and developing a robust incident response plan, these steps can significantly reduce your risk of a security breach. By prioritizing cybersecurity, you protect not only your data but also your organization’s reputation and financial stability.
In summary, the key practices include:
- Conduct regular security audits.
- Use strong password policies.
- Implement multi-factor authentication.
- Educate employees on cybersecurity.
- Keep software and systems updated.
- Backup data regularly.
- Use firewalls and antivirus software.
- Limit access to sensitive data.
- Develop an incident response plan.
- Monitor your systems.
By following these guidelines, your business can create a robust cybersecurity framework that will stand strong against the increasing tide of cyber threats.
